Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) , is an infrastructure-less wireless network that is deployed in a large number of wireless sensors in an ad-hoc manner that is used to monitor the system, physical, or environmental conditions.
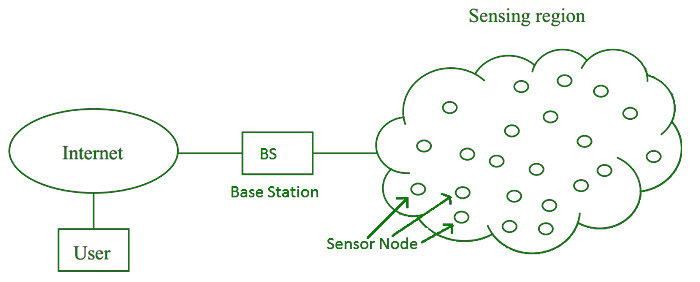
Sensor nodes are used in WSN with the onboard processor that manages and monitors the environment in a particular area. They are connected to the Base Station which acts as a processing unit in the WSN System. The base Station in a WSN System is connected through the Internet to share data. WSN can be used for processing, analysis, storage, and mining of the data.
Wireless Sensor Network Architecture
A Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) architecture is structured into three main layers:
- Physical Layer : This layer connects sensor nodes to the base station using technologies like radio waves, infrared , or Bluetooth . It ensures the physical communication between nodes and the base station.
- Data Link Layer : Responsible for establishing a reliable connection between sensor nodes and the base station. It uses protocols such as IEEE 802.15.4 to manage data transmission and ensure efficient communication within the network.
- Application Layer : Enables sensor nodes to communicate specific data to the base station. It uses protocols like ZigBee to define how data is formatted, transmitted, and received, supporting various applications such as environmental monitoring or industrial control.
These layers work together to facilitate the seamless operation and data flow within a Wireless Sensor Network, enabling efficient monitoring and data collection across diverse applications.
WSN Network Topologies
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) can be organized into different network topologies based on their application and network type. Here are the most common types:
- Bus Topology : In a Bus Topology, multiple nodes are connected to a single line or bus. Data travels along this bus from one node to the next. It’s a simple layout often used in smaller networks.
- StarTopology : Star Topology have a central node, called the master node, which connects directly to multiple other nodes. Data flows from the master node to the connected nodes. This topology is efficient for centralized control.
- Tree Topology : Tree Topology arrange nodes in a hierarchical structure resembling a tree. Data is transmitted from one node to another along the branches of the tree structure. It’s useful for expanding coverage in hierarchical deployments.
- Mesh Topology : Mesh Topology feature nodes interconnected with one another, forming a mesh-like structure. Data can travel through multiple paths from one node to another until it reaches its destination. This topology offers robust coverage and redundancy.
Each topology has its advantages and is chosen based on factors such as coverage area, scalability, and reliability requirements for the specific WSN application.
Types of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
Terrestrial Wireless Sensor Networks
- Used for efficient communication between base stations.
- Consist of thousands of nodes placed in an ad hoc (random) or structured (planned) manner.
- Nodes may use solar cells for energy efficiency.
- Focus on low energy use and optimal routing for efficiency.
- Nodes are buried underground to monitor underground conditions.
- Require additional sink nodes above ground for data transmission.
- Face challenges like high installation and maintenance costs.
- Limited battery life and difficulty in recharging due to underground setup.
Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
- Deployed in water environments using sensor nodes and autonomous underwater vehicles.
- Face challenges like slow data transmission, bandwidth limitations, and signal attenuation.
- Nodes have restricted and non-rechargeable power sources.
Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks
- Used to monitor multimedia events such as video, audio, and images.
- Nodes equipped with microphones and cameras for data capture.
- Challenges include high power consumption, large bandwidth requirements, and complex data processing.
- Designed for efficient wireless data compression and transmission.
Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks (MWSNs)
- Composed of mobile sensor nodes capable of independent movement.
- Offer advantages like increased coverage area, energy efficiency, and channel capacity compared to static networks.
- Nodes can sense, compute, and communicate while moving in the environment.
Each type of Wireless Sensor Network is tailored to specific environmental conditions and applications, utilizing different technologies and strategies to achieve efficient data collection and communication.
Applications of WSN
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Surveillance and Monitoring for security, threat detection
- Environmental temperature, humidity, and air pressure
- Noise Level of the surrounding
- Medical applications like patient monitoring
- Agriculture
- Landslide Detection
Challenges of WSN
- Quality of Service
- Security Issue
- Energy Efficiency
- Network Throughput
- Performance
- Ability to cope with node failure
- Cross layer optimisation
- Scalability to large scale of deployment
A modern Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) faces several challenges, including:
- Limited power and energy: WSNs are typically composed of battery-powered sensors that have limited energy resources. This makes it challenging to ensure that the network can function for long periods of time without the need for frequent battery replacements.
- Limited processing and storage capabilities: Sensor nodes in a WSN are typically small and have limited processing and storage capabilities. This makes it difficult to perform complex tasks or store large amounts of data.
- Heterogeneity: WSNs often consist of a variety of different sensor types and nodes with different capabilities. This makes it challenging to ensure that the network can function effectively and efficiently.
- Security: WSNs are vulnerable to various types of attacks, such as eavesdropping, jamming, and spoofing . Ensuring the security of the network and the data it collects is a major challenge.
- Scalability: WSNs often need to be able to support a large number of sensor nodes and handle large amounts of data. Ensuring that the network can scale to meet these demands is a significant challenge.
- Interference: WSNs are often deployed in environments where there is a lot of interference from other wireless devices. This can make it difficult to ensure reliable communication between sensor nodes.
- Reliability: WSNs are often used in critical applications, such as monitoring the environment or controlling industrial processes. Ensuring that the network is reliable and able to function correctly in all conditions is a major challenge.
Components of WSN
- Sensors: Sensors in WSN are used to capture the environmental variables and which is used for data acquisition. Sensor signals are converted into electrical signals.
- Radio Nodes: It is used to receive the data produced by the Sensors and sends it to the WLAN access point. It consists of a microcontroller , transceiver, external memory, and power source.
- WLAN Access Point: It receives the data which is sent by the Radio nodes wirelessly, generally through the internet.
- Evaluation Software: The data received by the WLAN Access Point is processed by a software called as Evaluation Software for presenting the report to the users for further processing of the data which can be used for processing, analysis, storage, and mining of the data.
Advantages
- Low cost: WSNs consist of small, low-cost sensors that are easy to deploy, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
- Wireless communication: WSNs eliminate the need for wired connections, which can be costly and difficult to install. Wireless communication also enables flexible deployment and reconfiguration of the network.
- Energy efficiency: WSNs use low-power devices and protocols to conserve energy, enabling long-term operation without the need for frequent battery replacements.
- Scalability: WSNs can be scaled up or down easily by adding or removing sensors, making them suitable for a range of applications and environments.
- Real-time monitoring: WSNs enable real-time monitoring of physical phenomena in the environment, providing timely information for decision making and control.
Disadvantages
- Limited range: The range of wireless communication in WSNs is limited, which can be a challenge for large-scale deployments or in environments with obstacles that obstruct radio signals.
- Limited processing power: WSNs use low-power devices, which may have limited processing power and memory, making it difficult to perform complex computations or support advanced applications.
- Data security: WSNs are vulnerable to security threats, such as eavesdropping, tampering, and denial of service attacks, which can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
- Interference: Wireless communication in WSNs can be susceptible to interference from other wireless devices or radio signals, which can degrade the quality of data transmission.
- Deployment challenges: Deploying WSNs can be challenging due to the need for proper sensor placement, power management, and network configuration, which can require significant time and resources.
- while WSNs offer many benefits, they also have limitations and challenges that must be considered when deploying and using them in real-world applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) are valuable systems that enable efficient monitoring and data collection across various applications. They play a crucial role in industries like environmental monitoring, healthcare, and agriculture by providing real-time data insights. Despite challenges such as energy efficiency and security, WSNs continue to evolve with advancements in technology, promising even more effective and reliable performance in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions on Wireless Sensor Network – FAQs
Where are Wireless Sensor Networks used?
WSNs are used in various fields such as environmental monitoring (like weather and pollution), healthcare (for patient monitoring), agriculture (crop monitoring), and industrial automation.
How do Wireless Sensor Networks work?
WSNs work by deploying sensor nodes in an area to collect data. These nodes communicate wirelessly with each other and with a central system or server, transmitting data for analysis and decision-making.
Can Wireless Sensor Networks be used for outdoor applications?
Yes, WSNs are suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications, depending on the specific environmental conditions and requirements of the deployment.
How secure are Wireless Sensor Networks?
Security measures such as encryption and authentication protocols are used to protect data transmitted within WSNs. However, ensuring robust security remains a continuous concern.


